Give your patients options
Qudexy® XR gives your patients options that immediate-release topiramate tablets don’t.
† Recommended dose for migraine prevention: 100 mg once daily.
100% extended-release bead formulation of topiramate.1,2

For illustrative purposes only.
Qudexy® XR capsules contain precisely engineered coated beads of topiramate. When the beads come in contact with gastrointestinal fluid, the fluid permeates through the extended-release coating, dissolving the topiramate, which allows it to slowly diffuse out through the coating to be absorbed.1,2
The release of the topiramate occurs continuously over an extended time frame. With once-daily dosing, its formulation composed of extended-release beads provides smooth topiramate levels over a 24-hour period, without the need for an immediate-release component.1,2
Delivers a Smooth Pharmacokinetic (PK) Profile
Qudexy® XR is an extended-release bead formulation of topiramate, providing a smooth PK profile.1,2
- Maintains topiramate levels for 24 hours with one dose daily
- 25% reduction in fluctuation of topiramate plasma concentrations compared to immediate-release topiramate††
- Reduces exposure to peak drug levels
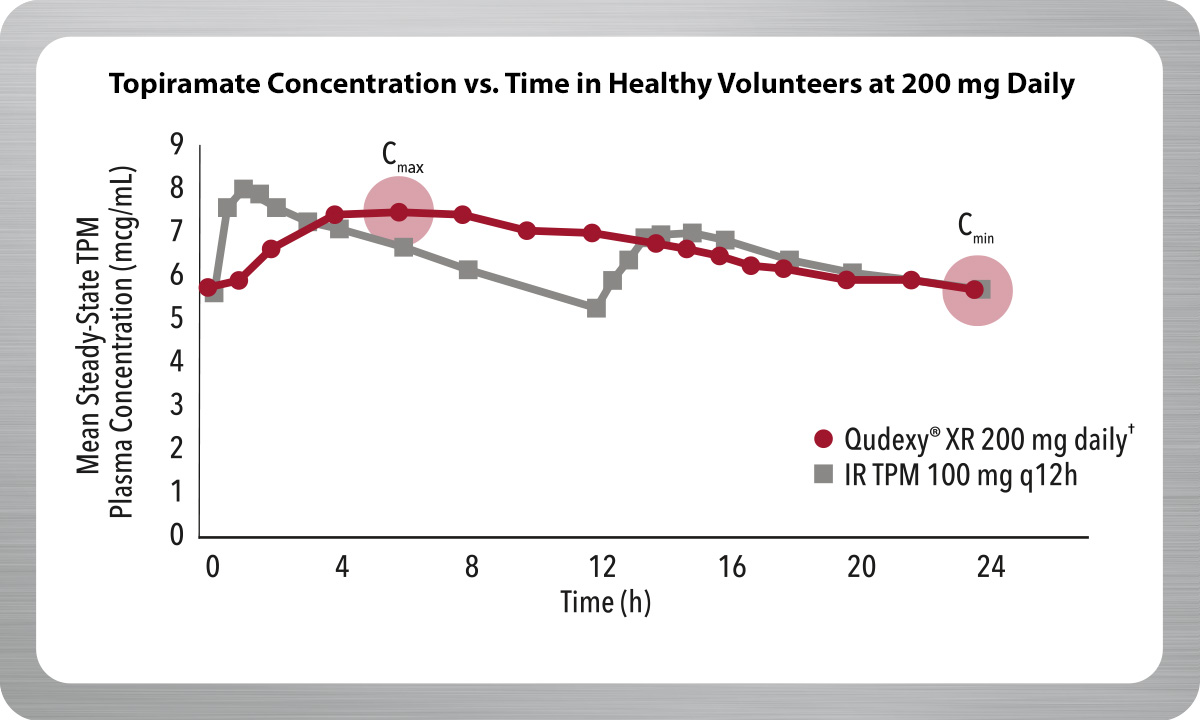
Result from a multiple-dose, crossover, bioavailability study of Qudexy® XR and IR TPM in 36 healthy volunteers.
†† Mean peak-to-trough fluctuation of TPM plasma concentrations at steady-state for Qudexy® XR was approximately 40% compared to approximately 53% for IR TPM.
† Recommended dose for migraine prophylaxis: 100 mg once daily.
IR TPM=immediate-release topiramate; Cmax=maximum plasma concentration; Cmin=minimum plasma concentration.
Maintains Concentrations After Switching From Immediate-Release Topiramate (IR TPM)
From day 1 after switching to Qudexy® XR, criteria for bioequivalence with IR TPM were met.§ 1,2
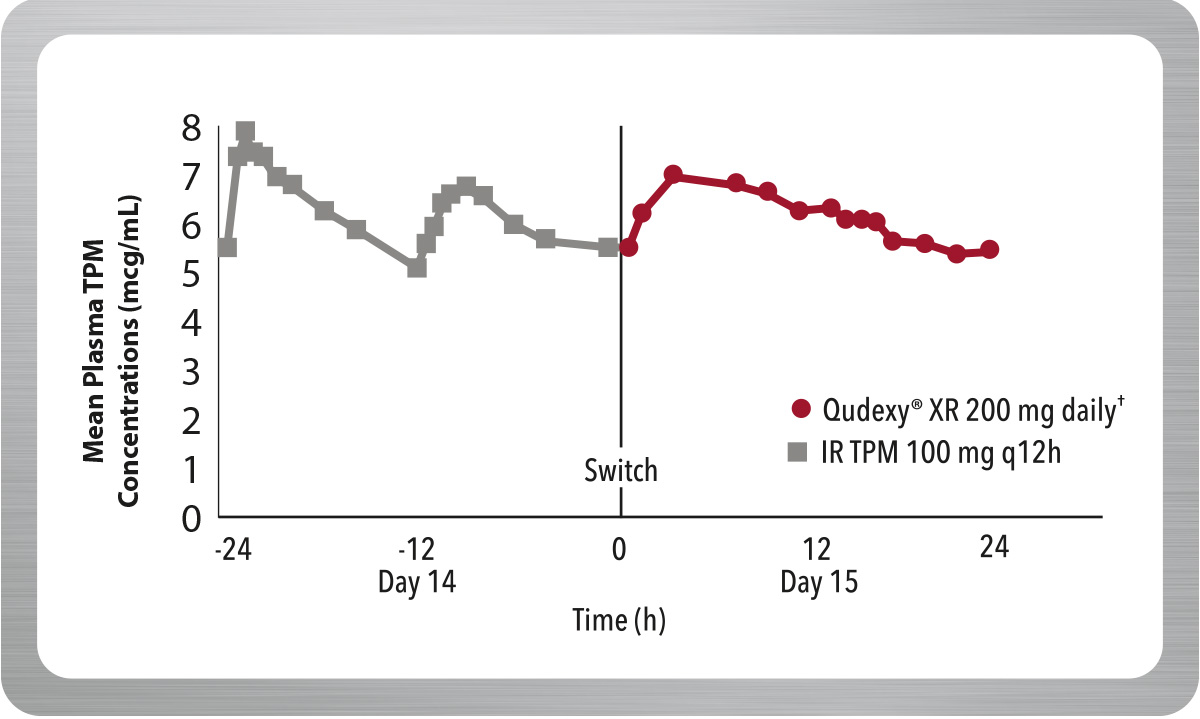
§ Switching between Qudexy® XR and IR TPM was evaluated in a multiple-dose, crossover, bioavailability study in 36 healthy volunteers. On the first day following the switch, there were no significant differences in AUC 0-24, Cmax and Cmin; the 90% CI for the ratios were contained within the 80–125% equivalence limits.
In addition, at steady state, the 90% Ci for the ratios of AUC0-24, Cmax and Cmin, as well as partial AUC for multiple time point, were also within the 80–125% bioequivalence limits, indicating no clinically significant difference between the formulations.
† Recommended dose for migraine prophylaxis: 100 mg once daily.
IR=immediate-release; TPM=topiramate; AUC=area under the curve; Cmax=maximum concentration; Cmin=minimum concentration; CI=confidence interval.
No Change in Total Daily Dose
Switch to a dosing schedule that works for your patients. No change in total daily dose is needed when converting from IR TPM to once-daily dosing with Qudexy® XR.2
-
IR TPM
- Total Daily Dose
- Morning
- Evening
50 mg 

100 mg 

150 mg 

200 mg 

Tablets shown are not exact size or color.
-
-
QUDEXY® XR
- Total Daily Dose
- Once Daily
25 mg 
50 mg 
100 mg† 
150 mg 
200 mg 
Capsules shown are not exact size or color.
† Recommended dose for migraine prophylaxis: 100 mg once daily.
PREVAIL Epilepsy Trial
Qudexy® XR is an extended-release topiramate formulation backed by PREVAIL Phase 3 data in patients with epilepsy.





 Rotate for Important Safety Information
Rotate for Important Safety Information